According to Dessler,
(2020) any organization is depending on people who is officially assigned
duties & responsibilities according to their job role. Managing of these
human asset in an effective manner according to the objectives of the
organization is Human Resource Management. Human Resource Management is a
process that involves acquiring, training, appraising & compensating while
handling labor relations, employee health/safety & fairness concerns.
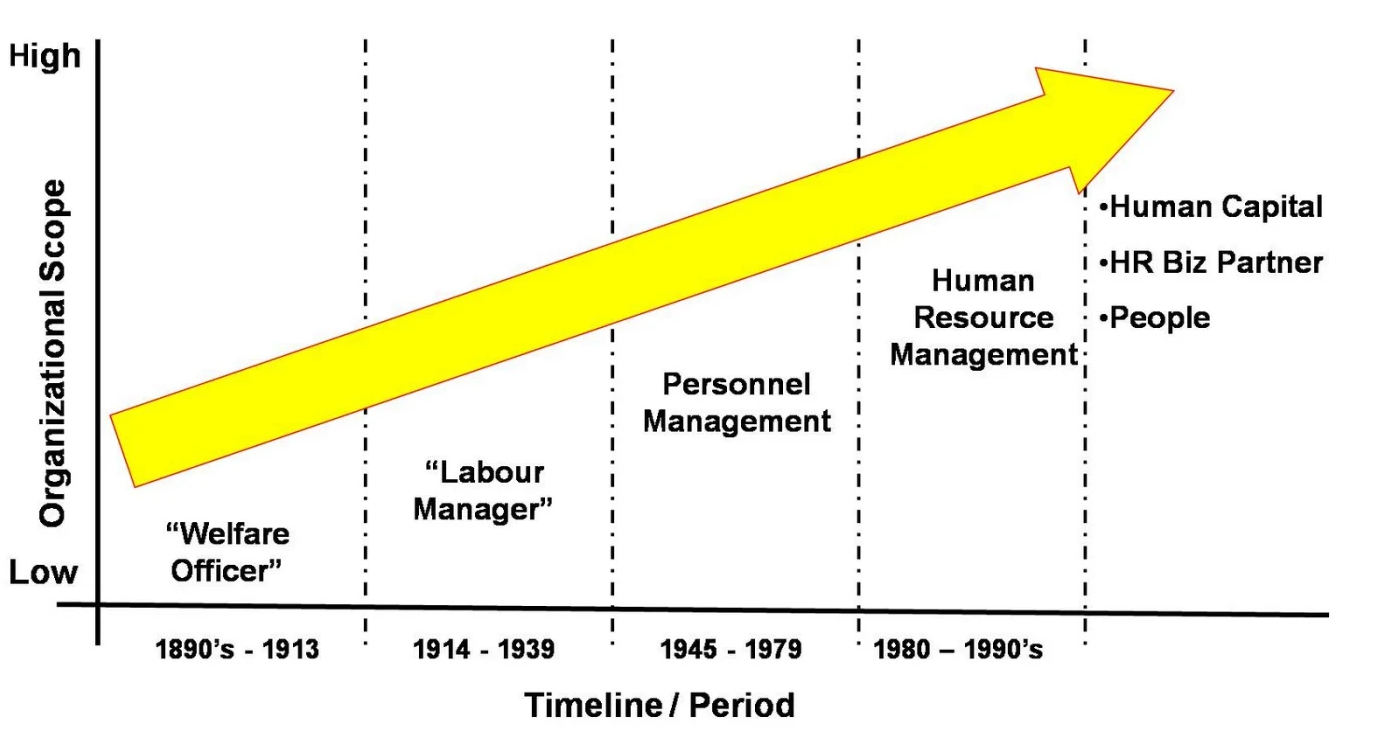
HRM was established
nearly a century ago in 1920, since than there have been continuous growth and
development in functions of human resource Management. Industrial revolution
was the inception for the evolution of HRM. Industrial revolution controlled
the behavior of the workers. Increase in production led to increase the
workforce and it demand for more policies to be adopted by mangers to regulate
the working environment. (Bal, 2011)
According to Jamrog &
Overholt, (2004) in early 19th century HRM was recognized as
scientific management methods where the employees were treated as machines and
management of human behavior was not considered under HRM.
Subsequently in 1960 HRM
transformed as one of the most recognized functions in the business environment
due to development of technology, economies, workforce and shifting of personal
management. During this era handling of payroll systems and staff grievances
was delegated to specialists. (Sammartino, 2002)
The latest concept of HRM
is the capability of withstanding the unpredictable challengers of the society
or refers as sustainability. To overcome this situation, the organization, need
to develop a strong framework of HRM strategies consisting of core policies and
practices. Accordingly, in a competitive environment organizations speedy
develop and the corporations need to move from physical technology to
information technology for effective and efficient HRM function. (Bansal, 2005);
(Freitas et al., 2011)
In contemporary context, HRM
departments in 21st Century are adopting to E HRM concepts all
around the world in rapid development in web based technologies. It manages the
whole lifecycle of the employee from its recruitment to exit. E HRM added more
Value to HRM functions to achieve competitive advantage for organizations today.
(Florowski & Olivasalujan, 2006)
(Figure 01 - Evolution of HRM)
References
Bansal, P. (2005) “Evolving sustainably: A
longitudinal study of corporate sustainable development,” Strategic Management Journal, 26(3),
pp. 197–218. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.441.
Dessler, G. (2020) Human Resource Management. 13th edn. New York: Pearson.
Florowski, G. and Olivasalujan, M.L. (2006) “ The
diffusion of human resource information-technology innovations in US and non-US
firms,” pp. 684–710.
Florowski, G. and Olivasalujan, M.L. (2006) The diffusion of human resource information-technology
innovations in US and non-US firms. Personnel Review,35(6),684-710
Jamrog, J.
and Overholt, M.H. (2004) “Building a strategic HR function: continuing the
evolution,” Human Resource Planning,
27(1), pp. 51–63.
Freitas, W.R.de S., Jabbour, C.J.C. and Santos, F.C.A.
(2011) “Continuing the evolution: Towards sustainable HRM and sustainable
organizations,” Business Strategy
Series, 12(5), pp. 226–234. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1108/17515631111166861.
Sammartino,
W. (2002) The system integration of
human resource management with organizational strategies. thesis.
Faculty of Economics, Business Administration and Accounting.
Yasemin Bal, (2011),“The new human resources management in the 21st century: a strategic view”, Annual conference
on innovations in Business &
Management, The Center for Innovations
in Business and Management Practices, London, UK, 2011

Comments
Post a Comment